Entlebucher Mountain Dog
Population Genetic Analysis
By Carol Beuchat PhD
June 2015
The pedigree database was supplied by Dru Patterson, President of the National Entlebucher Mountain Dog Association (US)
SUMMARY
*** The current population has the genetic equivalent of 4.8 dogs that are significantly more closely related than full siblings.
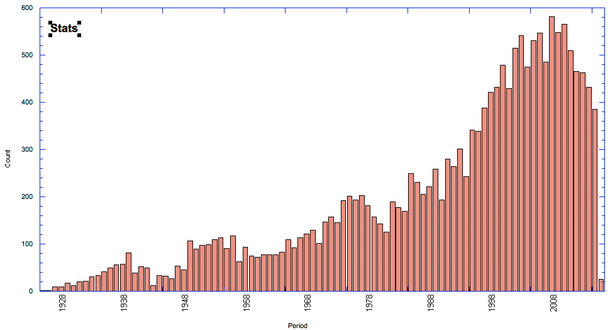
- Over the breed's history (as recorded in this database), the breed has produced a total of about 17,700 dogs, about 13% of which produced offspring. To maintain genetic diversity in a population of animals, it is recommended that at least 50% of the animals should contribute offspring to the gene pool.
- The current reproductive population has the genetic diversity expected of a population that was founded with 4.8 animals. It is recommended that this number should be at least 100
- Only 6% of the dogs in the current reproductive population have to date produced offspring recorded in the database.
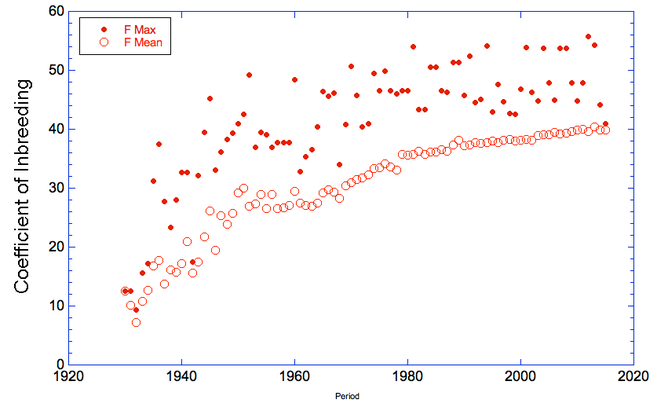
- The average level of relatedness (genetic similarity) of the animals in the current reproductive population is 38%. By comparison, the relatedness of full siblings is 25%.
- The effective population size of the current reproductive population is 162. The minimum size of a sustainably breeding population is about 1,000 randomly breeding animals.
*** The current population has the genetic equivalent of 4.8 dogs that are significantly more closely related than full siblings.
ANALYSIS DETAILS
For the entire pedigree database:
Total dogs in pedigree database = 17,690
Total males = 9,119
Total females = 8,552
Number of dogs with offspring = 2,264
Males with offspring = 761
Females with offspring = 1503
% of all dogs that were bred = 12.8%
% of all males that were bred = 8.3%
% of all females that were bred = 17.6%
Total males = 9,119
Total females = 8,552
Number of dogs with offspring = 2,264
Males with offspring = 761
Females with offspring = 1503
% of all dogs that were bred = 12.8%
% of all males that were bred = 8.3%
% of all females that were bred = 17.6%
For the current (potentially) reproductive population (dogs born since 2009)
Number of dogs = 2,848
Number of males = 1,459
Number of females = 1,387
Number of dogs with offspring = 176 (6.2%)
Males with offspring = 64 (4.4%)
Females with offspring = 112 (8.1%)
fe (effective number of founders) = 5.9
fa (effective number of ancestors) = 4.4
fg (founder genome equivalents) = 4.8
Ne (effective population size) = 162
average Mean Kinship = 38.8%
How to interpret population statistics
How small is too small?
Number of males = 1,459
Number of females = 1,387
Number of dogs with offspring = 176 (6.2%)
Males with offspring = 64 (4.4%)
Females with offspring = 112 (8.1%)
fe (effective number of founders) = 5.9
fa (effective number of ancestors) = 4.4
fg (founder genome equivalents) = 4.8
Ne (effective population size) = 162
average Mean Kinship = 38.8%
How to interpret population statistics
How small is too small?