PLUMMER TERRIER
Data are from a pedigree database supplied by Scott Robson that still needs to be edited for errors, so this information should be considered preliminary. Missing data or ID errors usually result in UNDERESTIMATES of inbreeding and kinship, so the numbers here (which are very high) should be considered to be more optimistic than the reality.
1688 dogs total
665 dogs with recorded offspring
36 "founder" dogs
fe = 11.4
fg = 7.6
fa = 5.9
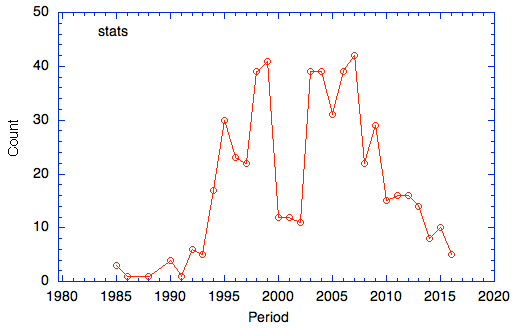
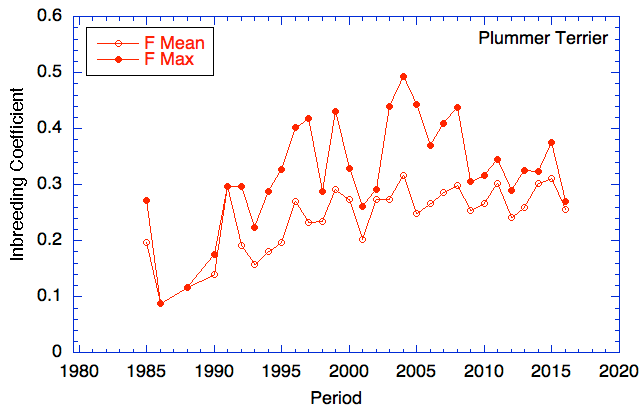
For the current population of dogs (approx generation 31 to present, about 2010-pres):
mean MK = 27%. If the dogs in the population were as closely related as full-siblings, this number would be 25%. Essentially any mating is the equivalent (or more) of a full sibling cross. (i.e., there are no "outcrosses").
9 ancestors account for all of the diversity in the breed; only 4 account for 77% (!!!).
Rollo W/C = 29%
Pip W/C = 22%
Vampire = 14%
Jenny = 12%
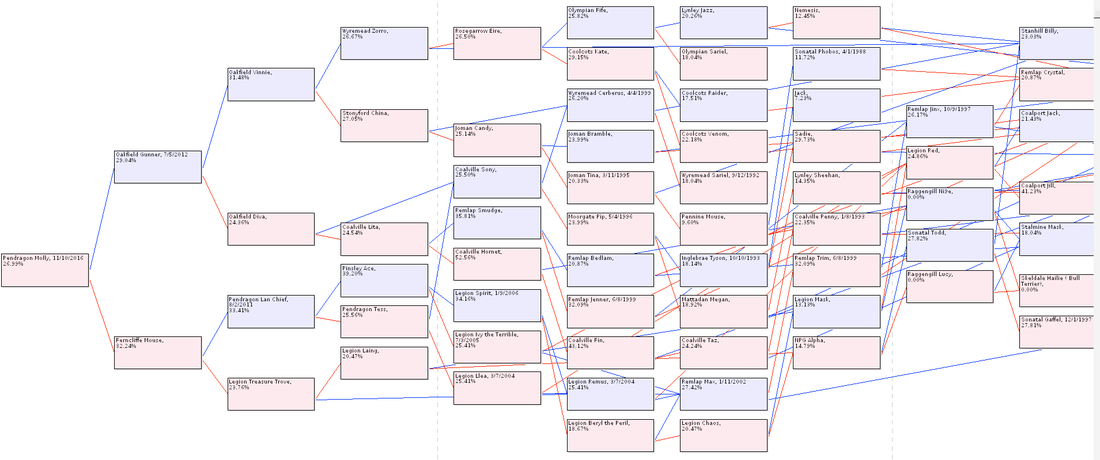
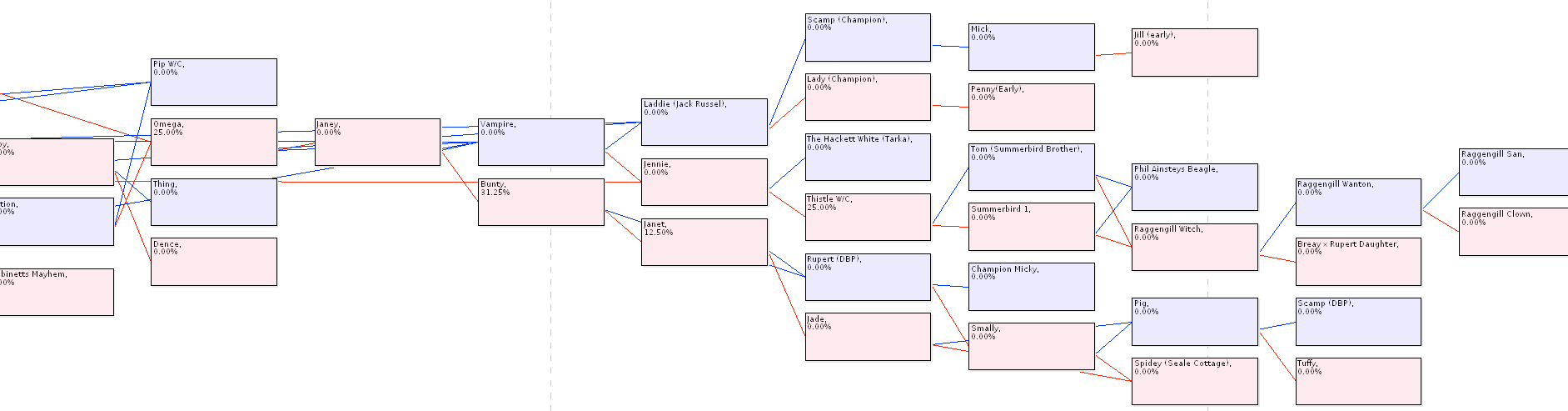
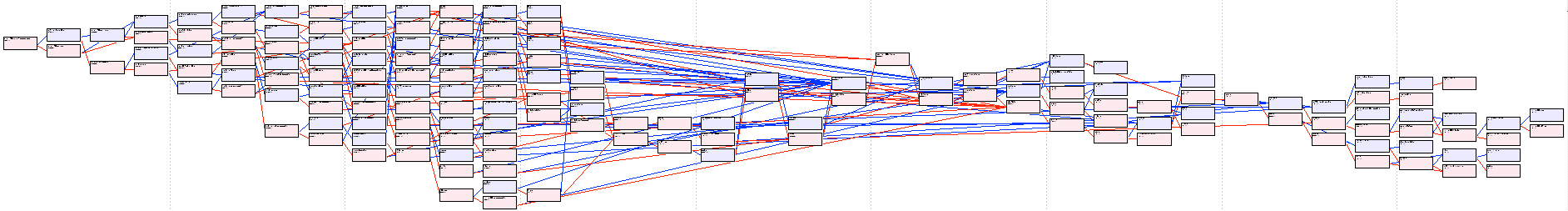
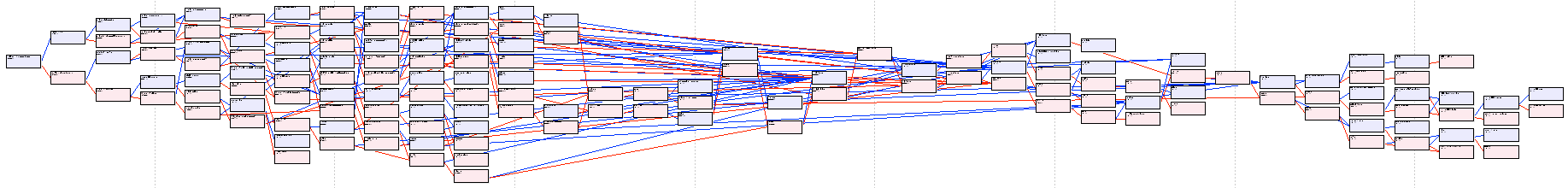
A few pedigree charts -
Pendragon Molly
top is the more recent generations (to the left), below are the founding dogs (to the right) (probably too small to read, though)
These pedigree charts clearly show the small number of founder dogs (on the right), several bottleneck generations (the "waists" in the middle of the charts), and recent inbreeding (on the left).