By oldest, I don't mean we've known about it the longest. When a dog has this form of cancer, the tumor cells themselves are 11,000 years old!
|
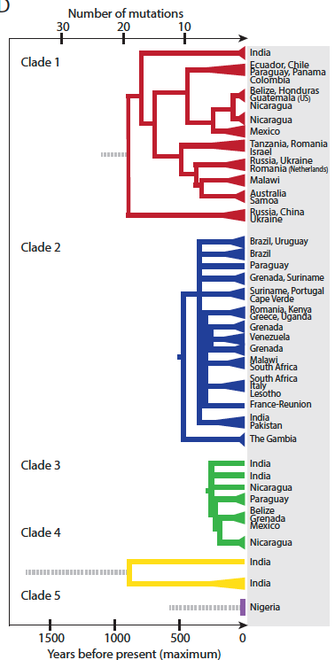
It took a bit of sleuthing to figure this out. The tipoff was in the mitochondria in the tumor cells. Mitochondria are inside the cells and are the power plants of life. They have their own DNA, and occasionally the mitochondria in the cancer cells can steal DNA from the normal cells of the dog. When this happens, it makes it possible to trace the lineage of cancer cells because of these unique bits of acquired DNA.
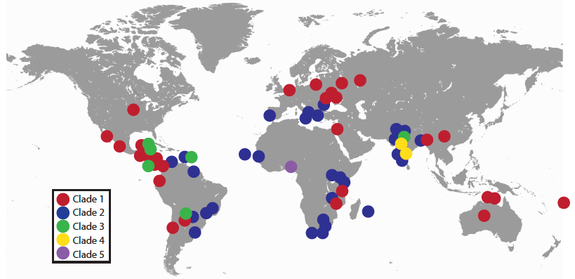
By examining the tumors from hundreds of dogs from around the world, researchers were able to determine that transfer of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has occurred at least five times. This left the tumor DNA with a unique genetic signature from each DNA swap that allowed these specific lines of cancer cells (called "clades") to be traced around the world.
The data suggest that that the oldest clade of cancer cells cancer spread from China or Russia about 1,000 years ago, probably via dogs that were traveling with humans. The cancer appeared in America within the last 500 years, probably arriving with the conquistadors, and reached Australia in about 1900 traveling in dogs brought by European settlers.
As if the story of this ancient, contagious cancer wasn't unusual enough, researchers found dogs in which the canine and tumor mtDNA had actually recombined - something that has never been observed before.
Transmissible cancers like the venereal cancer that occurs in dogs are rare in nature. There are two transmissible cancers that can infect the Tasmanian Devil in Tasmania one found in shellfish, and one that occurs in captive Syrian hamsters.
|
ICB's online courses
***************************************
Visit our Facebook Groups
ICB Institute of Canine Biology
...the latest canine news and research
ICB Breeding for the Future
...the science of dog breeding